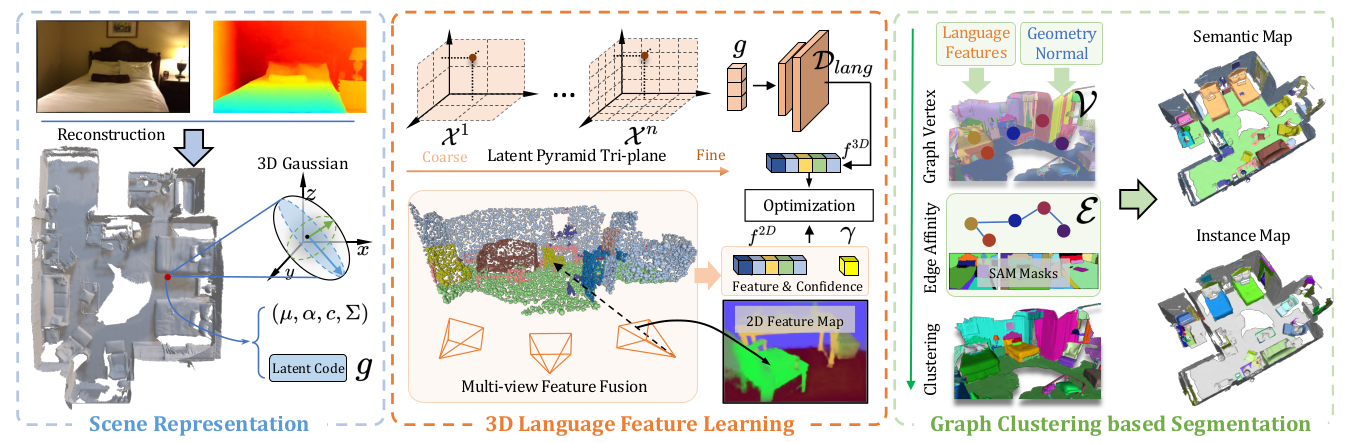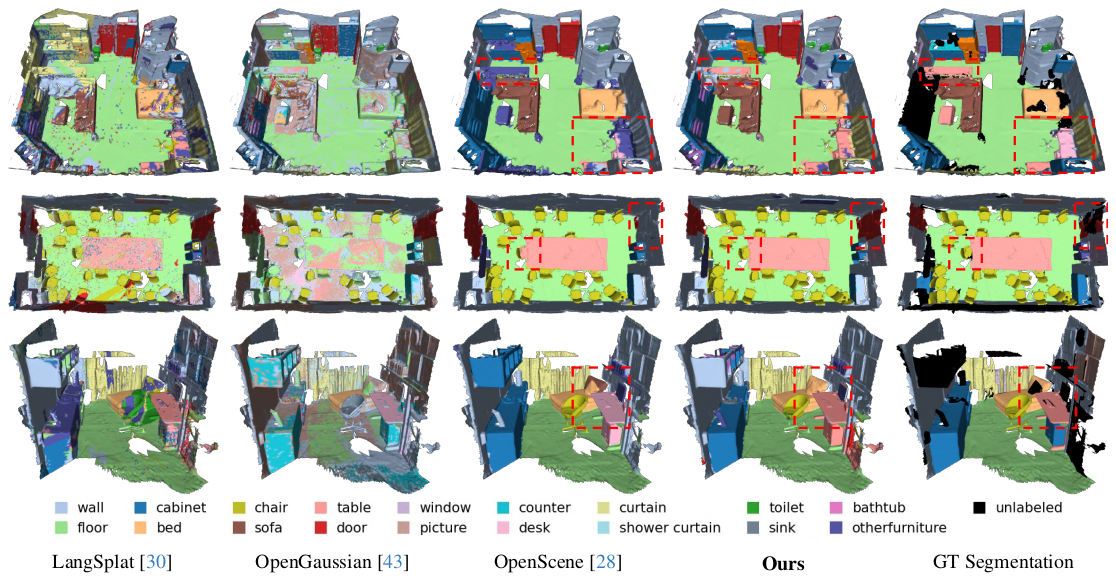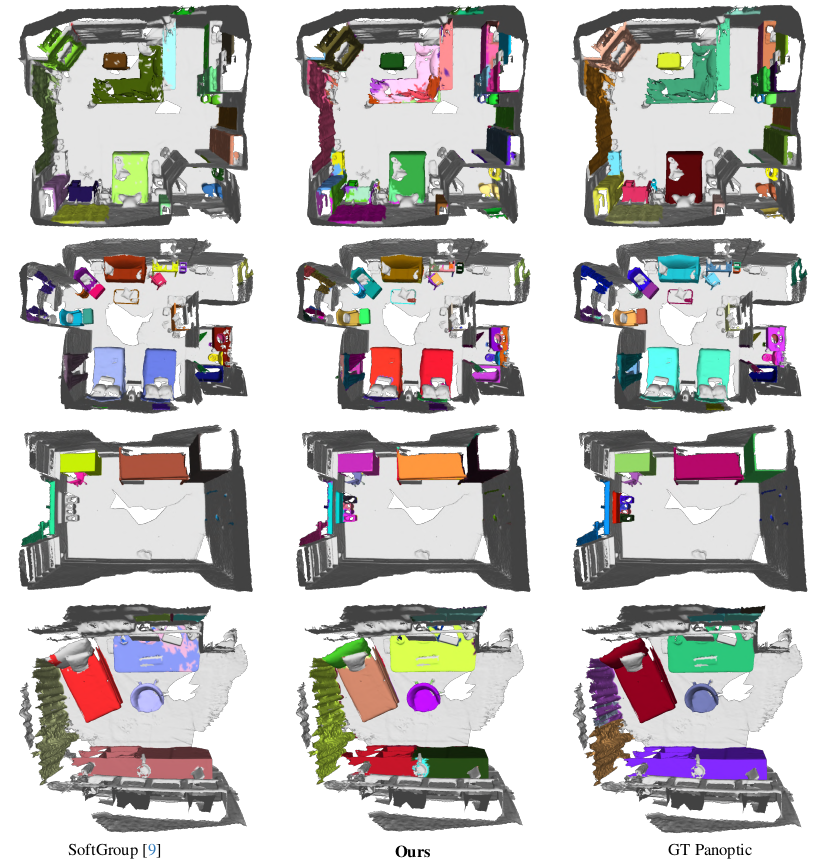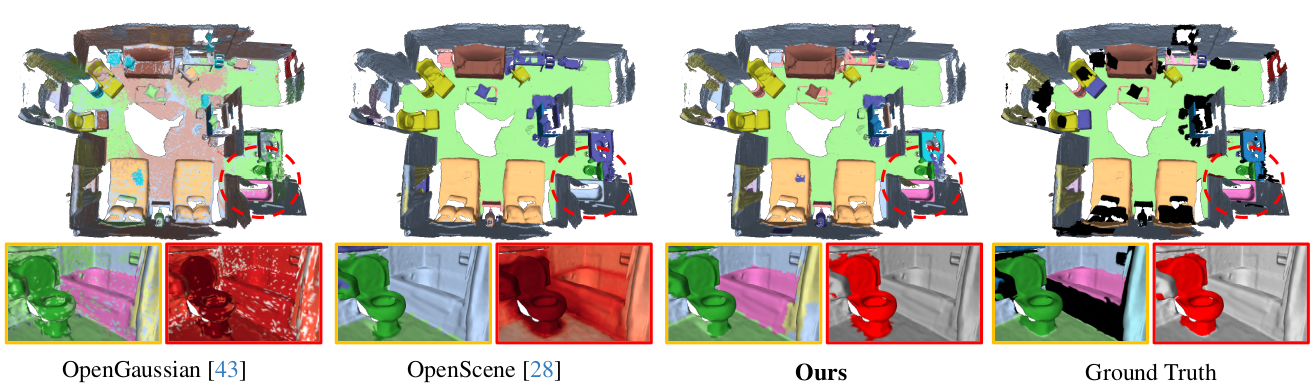
We propose PanoGS, a novel and effective 3D panoptic open vocabulary scene understanding approach. Our PanoGS can achieve more accurate segmentation results and generate 3D instance-level results for open-vocabulary text queries, unlike previous methods that generate heatmaps between scene features and text queries